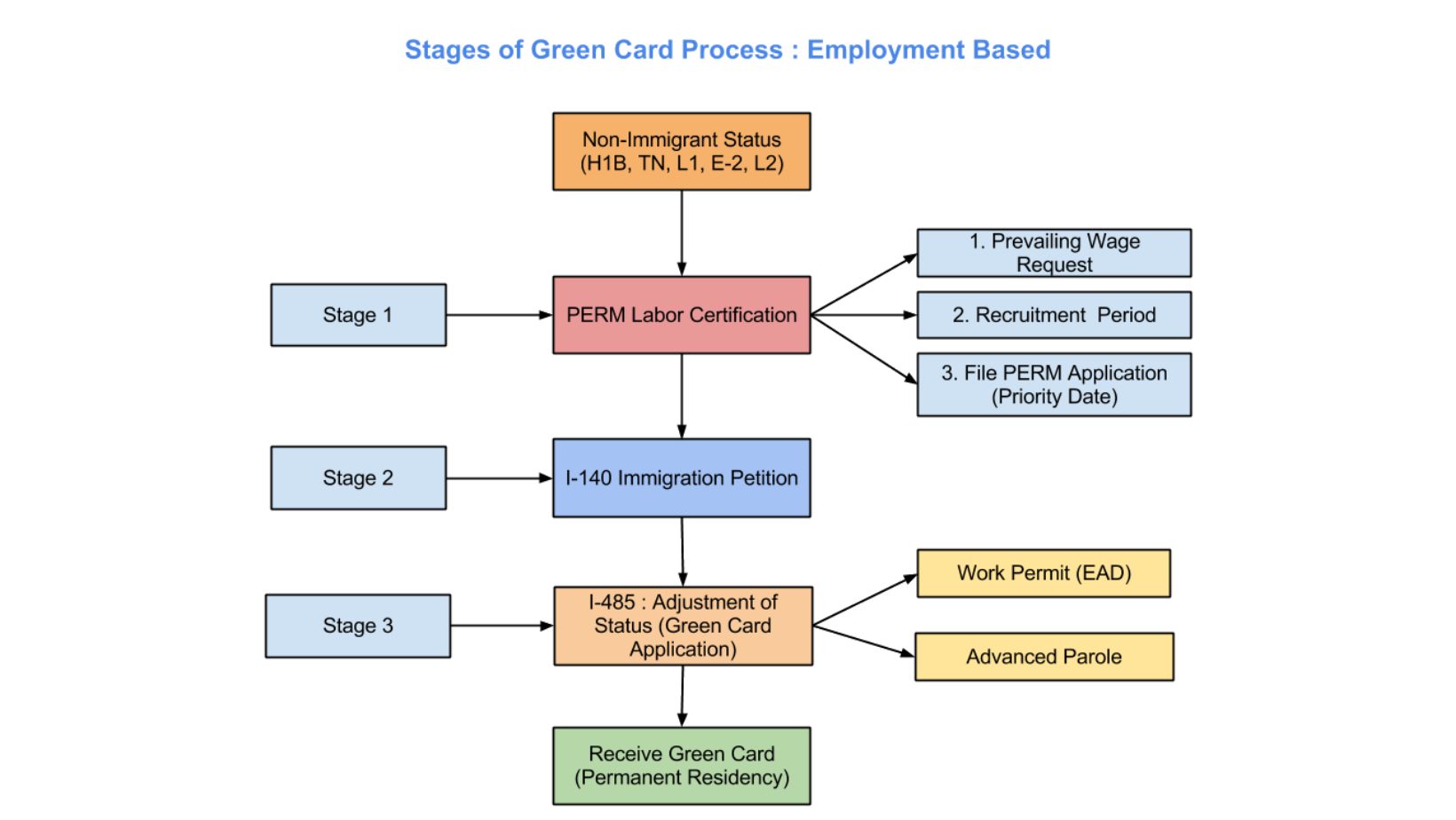
PERM Labor Certification Process Explained: Steps and Requirements
Central to your journey of getting a green card through employment in the US is the PERM (Program Electronic Review Management) Labor Certification process. If an employer wants to sponsor your employer-based green card under the EB-2 or EB-3 category, the first step under PERM (Program Electronic Review Management) Labor Certification process is to request Prevailing Wage Determination through the National Prevailing Wage Center (NPWC).
The National Prevailing Wage Center (NPWC) which is a branch of the DOL that provides prevailing wage determinations, which dictate the minimum salary that must be offered for the specific position.
The PERM Process is critical for certain employment-based permanent residency applications. This process is administered by the US Department of Labor (DOL), to protect the US labor market. It guarantees that employing skilled foreign workers doesn’t cause a hit to employment opportunities, wages, and working conditions of US workers in similar roles.
In short, employers must acquire a PERM Labor Certification before the I-140 form (Immigrant Petition for Alien Worker) is filed with the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
This sequential approach ensures a tightly regulated yet fair immigration system that balances the aspirations of foreign workers with the integrity of the American workforce.
Key Functions of the PERM Process
This protocol is designed with a dual objective. It ensures that hiring workers who are non-US citizens genuinely fills in gaps in the US workforce without displacing or detrimentally affecting the employment conditions of American workers. Here are the key functions of the PERM process:
Prevailing wage determination: This process begins with obtaining a prevailing wage determination from the DOL. This step verifies that wages offered to foreign workers are commensurate with those of similarly employed US workers in the employment region. This stipulation prevents the undercutting of wages that could otherwise harm the local labor market.
Labor market test: At its core, the PERM process acts as a regulator for the local labor market. It mandates that employers perform extensive recruitment efforts to first identify US workers for job opportunities. If unsuccessful, it demonstrates the position couldn’t be filled by domestic workers with the necessary skills available for the prevailing wage.
Protecting working conditions: By enforcing equitable wage standards, the PERM process protects the working conditions within specific industries. This prevents the dilution of labor conditions that may occur if lower-wage foreign workers were employed under less stringent regulatory oversight.
Book a Consultation to Determine Your Eligibility
Note: It is important to note that the PERM can only be initiated by an employer. The employee cannot sponsor the green card process through PERM themselves.
Requirements for a PERM Labor Certification
Here’s an extended list of requirements for a PERM Labor Certification process:
Ensure job duties and qualifications are customary to the occupation and not tailored to the foreign worker’s qualifications.
Submit form ETA-9141 to obtain the prevailing wage for the job.
After the prevailing wage determination is issued (in some cases while it is pending), the employer can initiate the labor market test which includes:
Place a job order with the State Workforce Agency (SWA) for a minimum of 30 days.
For professional positions, conduct three additional recruitment methods. Some examples include job fairs, posts on the employer’s website, job search websites, on-campus recruiting, private employment firms, employee referral programs with incentives, local and ethnic newspapers, and professional associations.
Maintain documentation of the recruitment process, including advertisement copies, recruitment reports, and corresponding results of recruitment drives.
Attest that employment of the foreign worker won’t impact the wages and working conditions of similarly employed US workers.
Confirm there haven’t been layoffs in the same or similar job classifications within the area of intended employment within six months before the application or recruitment.
Be prepared to respond to potential audits by promptly providing supporting documentation.
The employer pays a minimum of 100% of the existing wage. Also, these wages must not include any monetary incentives, commissions, or bonuses.
The employer must be able to add potential foreign workers to its payroll on or before their arrival date in the US.
Complete ETA Form 9089 with detailed and accurate information about the job offer, recruitment process, and reasons for rejecting US applicants.
Employer Must Give Notice Before Submitting a PERM Application
The employer must put forth a notice before submitting the PERM forms. Either a union representative of the present workers or the employees themselves must receive this notice. Here are some standard rules for submitting the notice:
Must be submitted 1-6 months before filing the PERM application.
The wages offered and mentioned must be equal or higher than the prevailing wage or actual wage for the position.
Must include the application handler’s, also known as the Certifying Officer’s, address.
Must highlight that any party can send proof about the PERM application directly to the Certifying Officer.
Only after these details are attended to in the notice can the PERM application be filed.
The PERM Application
The main documentation of the PERM process is Form ETA 9089. This is filed electronically with the DOL, and the employer must provide detailed information about the job duties, requirements, recruitment process, reasons US workers weren’t hired, etc.
Note: For those using postal services to submit form ETA 9089, the signatures of the non-US citizen beneficiary, employer, and application bearer are mandatory.
It’s also necessary that all assembled paperwork during the PERM application must be carefully kept for at least five years. This helps with future auditing tasks.
Remember, the form requires a bunch of other job and employee details. Since the employer usually handles this, we won’t be elaborating on them. Just in case you’re wondering, here are some data points required:
Business name and founding details, and employer’s 9-digit Employer Identification Number (EIN)
Source (appropriate SWA body) of the prevailing wage
Extensive recruitment details
Employee’s language and educational requirements
The employer can deliver their application upon completion of the above form ETA 9089.
How Long Does It Take to Process the PERM Application?
The DOL processes your PERM application in approximately 10-13 months. Employers can use the Permanent Online System for quicker acceptance. Keep in mind that such online applications help with faster processing times, easier tracking, reusing information readily, and assessing existing copies of previous forms.
Note: PERM applications selected for audit can take approx. 17 months.
What if the PERM is denied?
If the PERM is denied, there might be recourse available in the form of filing an appeal with BALCA (Board of Alien Certifications Appeal). I will be sharing details about the process in a separate article.
Stay tuned if your PERM application is rejected, we’ll be sharing another blog on this soon.
And speak to our consultants if you’ve already faced a PERM rejection.
How Much Does the PERM Application Cost?
The PERM application is free of cost. You can still expect these associated overhead charges:
$715 for the I-140 form
$3000-$4000 attorney fees
$1000-$5000 for recruitment drives depending on the geographical location of the job opportunity (including digital and newspaper ads and sponsored job postings on online job portals)
Steps After PERM Approval
Here’s what happens after your PERM is approved:
Employer Submits I-140 for Employee Green Card
Upon DOL certification on Form 9089, the employer may file Form I-140 with the USCIS to classify the foreign worker under the correct employment-based (EB) preference category. This essentially facilitates the green card procedure for non-US citizens applying for EB visas.
Employer must submit I-140 within six months of the PERM application being approved
Employer must prove their capability to clear wages as per the above rules
Employer must clearly verify that the foreign worker has the relevant skills, education, and experience
Remember that the USCIS can take anything from 4-6 months to process the I-140. Feel free to expedite the procedure via a premium processing option that processes your documents in 15 days for a fee of $2805.